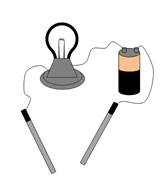

Have you ever seen an electrical conductivity tester like the one pictured here? Depending on the solution that the probes are placed in, the bulb will light up. What type of solution would make the bulb glow?
![]() Watch this video to determine the answer to this question.
Watch this video to determine the answer to this question.
Source: Electrolytes, CPDEatUCO, YouTube
In order for an electric current to be present, electrons must be able to move freely. The ions that have dissociated in the electrolytic sodium chloride solution allow the current of electrons to flow and the light bulb to be lit. In the non-electrolytic sucrose solution, there are no ions present, and the electrons cannot move in solution.

Source: Conductivity Meter, Cole-Palmer
A conductivity meter is used to measure the amount of current that can be conducted by a solution. There are several different types and brands of conductivity meters like the one pictured here. All conductivity meters work the same way; they measure the number of ions in a solution. The more ions present in the solution, the more conductive the solution and the higher the reading on the conductivity meter.
![]() Below, there are three conductivity readings and three beakers containing the same volume of a .001 molar solution. Look carefully at the chemical formulas on the beakers. In your notes, predict which conductivity readings will match the solutions. Click on the beakers to place the conductivity meter in each beaker, and check your predictions.
Below, there are three conductivity readings and three beakers containing the same volume of a .001 molar solution. Look carefully at the chemical formulas on the beakers. In your notes, predict which conductivity readings will match the solutions. Click on the beakers to place the conductivity meter in each beaker, and check your predictions.
In your notes, describe the results from the lab and explain the conductivity of each solution.
