Additional Resources
Please note that the resources open in a new window/tab in your browser. To return to this lesson, close the additional resource window/tab.
Deriving the Formula - Volume of Pyramid
A video showing the volume of a pyramid and a prism.
Deriving the Formula - Volume of Cone
A video showing the volume of a cone and cylinder.
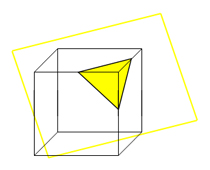
Cross Sections
Interactive showing the cross sections of a cube.
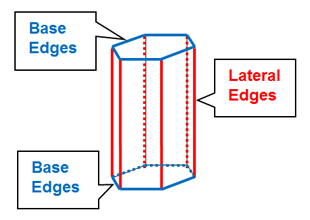
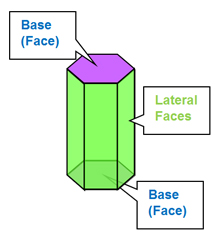
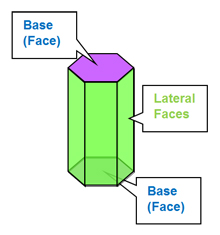
3D Shapes: Prisms
An exploration of prisms.
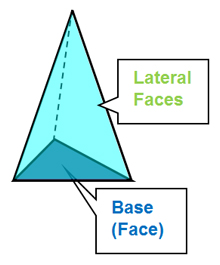
3D Shapes: Pyramids
An exploration of pyramids.
Platonic Solids
An exploration of Platonic solids.
Platonic Solids Nets
This site includes printable nets that can be used to create models of Platonic solids.
Assessment Feedback
Feedback for question number five in the lesson assessment.
Resources Used in This Lesson
Euler's Theorem
A description of Euler's Theorem.
Volume Enclosed by a Cube
An interactive demonstrating how to find the volume of a cube.
Volume of a Rectangular Prism
This page demonstrates how to find the volume of a rectangular prism.
Volume Enclosed by a Cylinder
This page demonstrates how to find the volume of a cylinder.
Platonic Solids Slicing
A demonstration of slicing solids.
Glossary