Example: |3| = 3 or |-3| = 3
If nx = a, the logarithm of a, n is the base.
Examples: (x - 2) or (3x + 5)
logb (ARGUMENT) = log (ARGUMENT) log b
If k = y x or y = kx, where k is a non-zero constant, then y varies directly with x.
x(a + b) = ax + bx
The set of points for which the sum of the distances to two foci within the curve are congruent.
In this example: 82 = 8 × 8 = 64 or x2 = x × x.
The rate of decay is proportional to the y-value, so as the y-values get smaller, the graph flattens out (or approaches a horizontal asymptote).
The rate of decay is proportional to the y-value, so as the y-values get larger, the graph grows without bound (or exponentially).
The distance from the focus to the parabola is equal to the distance from the directrix to the parabola.
A function f(x) can be moved “h” units right/left by performing the operation f(x ± h).
It is the locus of points for which the difference of the distances from two given points is a constant.
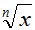 ; radical √x has an index of 2 and is often called the square root of x
; radical √x has an index of 2 and is often called the square root of xIf xy = k or . y = k xwhere k is a non-zero constant, then y varies inversely with x.
If nx = a, the logarithm of a, with n as the base, is x.
These functions can be rewritten without logarithms in the equivalent statement: x = By Only positive real numbers have real logarithms. You cannot take the logarithm of a negative number. For instance, y = log2(-4) is undefined since the equivalent statement: -4 = 2y has no solution. You cannot raise 2 to any power (y) to generate -4 as the answer.
"Matrices" is the plural form of "matrix".
Perfect squares factor into either the square of a sum such as (x + 3)2, or the square of a difference such as (x - 9)2.
The general form is: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c.
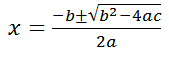 which gives solutions or roots for equations of the
form ax2 + bx + c (a ≠ 0)
which gives solutions or roots for equations of the
form ax2 + bx + c (a ≠ 0)Example: √x
There needs to be a variable in the denominator to be a rational function.
All entries above and below the diagonal are 0’s.
Only the location of the graph changes, the shape stays the same.
A function f(x) can be moved “k” units up/down by performing the operation f(x) ± k.
Example: If (x + 1)(x + 2) = 0, then (x + 1) = 0 or (x + 2) = 0.