You may recall from your middle school mathematics courses that there are four basic transformations. The four basic transformations are:

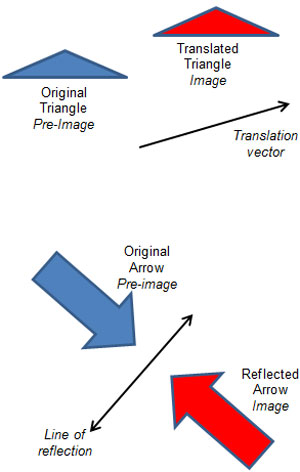
Translation – slides each point of a figure the same distance in the same direction. The blue triangle is translated to generate the red triangle in the direction of the arrow shown. The blue triangle is the pre-image and the red triangle is the image. In some textbooks, the arrow indicating the direction and distance of the translation is called a translation vector.
Reflection – flips the figure, including all of the points that make up the figure across a line of reflection.
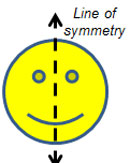
A reflection within a figure creates symmetry within that figure, where half of the figure is reflected onto the other half. In this case, the line of reflection is called a line of symmetry.
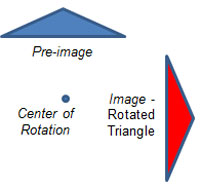
Rotation – turns a figure, and all of the points contained in that figure, around a point. The point is called a center of rotation.
Dilation - a figure is enlarged or reduced or stretched or shrunk using a scale factor that is not equal to 0. A dilation is typically given with respect to a center of dilation.
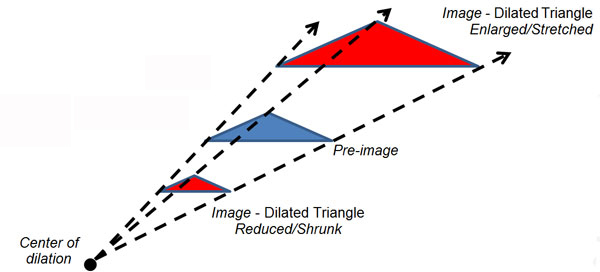
A figure that is dilated with a scale factor between 0 and 1 is also called a reduction, and a figure that is dilated with a scale factor greater than 1 is also called an enlargement.
To summarize, fill in the blanks.
![]() Examples
Examples