In addition to optical and radio telescopes, there are other types as well.
Infrared telescopes work by detecting infrared light. Infrared energy is sensed as heat. Objects such as humans and other animals emit infrared waves. Because human eyes cannot see infrared waves, we have to use special tools to “see” them. Night vision goggles and infrared cameras allow us to “see” infrared rays emitting from objects such as humans and animals. Something that is warm looks bright in infrared, while cooler objects look dark in infrared.
![]() Watch this video to learn more about infrared light and how astronomers use it to learn about objects in the universe.
Watch this video to learn more about infrared light and how astronomers use it to learn about objects in the universe.
Source: Infrared: More Than Your Eyes Can See, SpitzerJim, YouTube
Since the time this video was published, many telescopes with infrared cameras have been used by astronomers to observe objects in the universe. For example, the picture below shows a nebula as seen from both an optical light telescope and an infrared telescope.
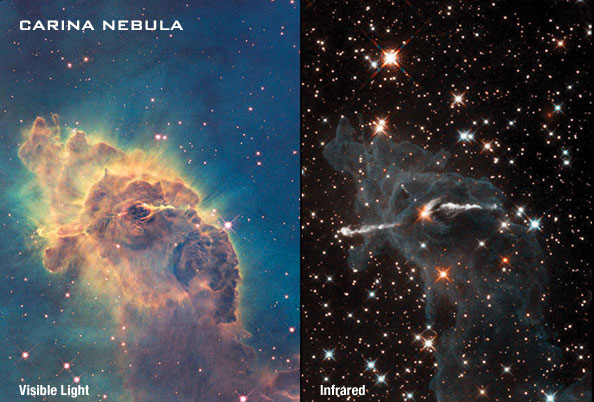

Source: Carina Nebula, NASA
Ultraviolet telescopes, positioned above the atmosphere, orbit around Earth and sense the ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun. The image below shows the sun from an ultraviolet telescope.
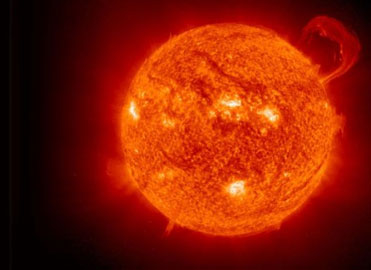
Source: Sun Extreme Ultraviolet Imaging, Free Wallpapers free
Many things in space give off X-rays; among them are black holes, neutron stars, binary star systems, comets, and stars, including the Sun. According to NASA, "the first X-ray telescope used in astronomy was to observe the sun. The first X-ray picture of the sun, by a rocket-borne telescope, was taken in 1963. The first orbiting X-ray telescope flew on Skylab in the early 1970s and recorded over 35,000 images of the sun." The picture below shows the sun taken by an X-ray telescope.

Source: Sun by an X-Ray Telescope, NASA
Gamma ray telescopes are designed to detect gamma rays from sources outside Earth's atmosphere. Unlike other types of waves, gamma rays cannot be captured and reflected by mirrors. Gamma rays are detected by the optical flashes they produce when interacting with the material. The first gamma ray telescope was carried on board the American satellite Explorer 11 in 1961. Gamma ray telescopes are designed to study celestial bodies with high energy, such as white dwarf stars, neurons stars, and black holes. The picture below shows a gamma ray burst.

Source: Gama Ray Burst, My Dark Sky
Scientists use images from all types of telescopes to study the objects of the universe. In fact, most of the modern satellites and observatories use more than one type of telescope.