If a light ray strikes the surface of a flat mirror at a 40° angle from the normal, the reflected light ray will be —
A. 40 degrees from the surface of the mirror.
Incorrect. The angle of reflection off of a flat mirror will be the same as the angle of incidence. Be careful to read the answer choice to see if the angle is given from the surface of the mirror or from normal.
B. 40 degrees from the normal.
Correct! The angle of reflection off of a flat mirror will be the same as the angle of incidence.
C. 50 degrees from the normal.
Incorrect. The angle of reflection off of a flat mirror will be the same as the angle of incidence. Be careful to read the answer choice to see if the angle is given from the surface of the mirror or from normal.
D. unable to determine from the information given.
Incorrect. There is enough information given in the problem to determine an answer. The angle of reflection off of a flat mirror will be the same as the angle of incidence.
Light is traveling through air and strikes the surface of water at an angle of 20° from the normal. As the light moves from the air into the water, it will —
A. continue traveling in a straight line making an angle of 20 degrees to the normal.
Incorrect. Since the light slows down as it enters the water, the light ray will bend toward the normal, so the angle of refraction will be less than 20 degrees.
B. follow a random path that cannot be predicted.
Incorrect. Since the light slows down as it enters the water, the light ray will bend toward the normal, so the angle of refraction will be less than 20 degrees.
C. bend away from the normal at an angle greater than 20 degrees.
Incorrect. Since the light slows down as it enters the water, the light ray will bend toward the normal, not away.
D. bend toward the normal at an angle less than 20 degrees.
Correct! Since the light slows down as it enters the water, the light ray will bend toward the normal.

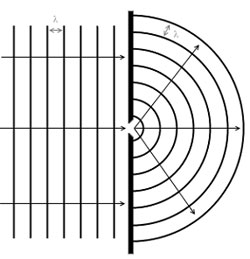
The diagram above represents water waves in a ripple tank. The two rectangles represent barriers with a small opening between them. The waves are traveling from left to right. As part of the wave front on the left passes through the opening between the barriers, the wave front begins to spread out around the edges of the barrier. This phenomenon is known as —
A. reflection
Incorrect. While some of the original parallel waves on the left will be reflected back by the barriers toward the right, the questions asks about the wave activity on the right side of the diagram. This diagram represents diffraction since the waves are passing by the edges of the barriers and are spreading out behind the barriers.
B. refraction
Incorrect. Refraction occurs when waves travel through one medium and move into a second medium at an angle and bend. The waves in the diagram are not moving into a new medium. This diagram represents diffraction since the waves are passing by the edges of the barriers and are spreading out behind the barriers.
C. diffraction
Correct! The waves in the diagram are passing by the edges of the barriers and are spreading out behind the barriers.
D. resonance
Incorrect. Resonance has to do with an increase in vibration of a medium caused when a periodic force is applied to the medium that matches the medium’s natural frequency. There is no evidence of resonance in this diagram. This diagram represents diffraction since the waves are passing by the edges of the barriers and are spreading out behind the barriers.
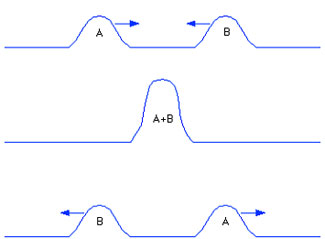
In the diagram above wave pulse A is moving toward the right and wave pulse B is moving toward the left. Notice that the amplitudes are both on the same side of the equilibrium position. As these waves interact, what type of interference is being shown?
A. constructive interference
Correct! Since the waves’ amplitudes are on the same side of the equilibrium position, the superposition principle says that they will reinforce each other resulting in constructive interference. Notice how the amplitude of A+B is bigger than the individual amplitudes of A or B.
B. destructive interference
Incorrect. For destructive interference to occur, the amplitudes have to be on opposite sides of the equilibrium position. This diagram shows constructive interference since the amplitudes are on the same side of the equilibrium position and reinforce each other. In destructive interference, the waves partially or totally cancel each other out.
C. no interference
Incorrect. If there was no interference, there would be no change in the waves’ amplitudes. In the diagram the A+B are clearly shows larger amplitude, so this is an example of constructive interference.
D. resonance
Incorrect. Resonance is one vibration driving another; this is building of two wave pulses.
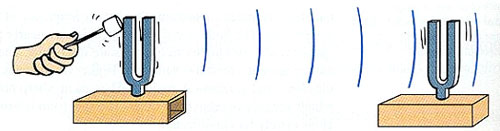
Both tuning forks in the diagram above have natural frequencies of 256 Hz. Someone strikes the tuning fork on the left with a rubber hammer which causes it to start vibrating. The tuning fork on the right then begins to vibrate, too, without being hit by the rubber hammer. What property is the tuning fork on the right exhibiting?
A. interference
Incorrect. There is no evidence of interference. The tuning fork on the right is vibrating due to resonance because the frequency of the sound waves coming from the tuning fork on the left matches the natural frequency of the tuning fork on the right.
B. resonance
Correct! The tuning fork on the right is resonating due because the frequency of the sound waves coming from the tuning fork on the left matches its natural frequency.
C. diffraction
Incorrect. Diffraction is when waves pass an obstruction and move behind it. While there may be some diffraction of sound, the problem is focusing on the vibration of the tuning fork on the right. It is vibrating due to resonance because the frequency of the sound waves coming from the tuning fork on the left matches the natural frequency of the tuning fork on the right.
D. this situation cannot occur
Incorrect. Diffraction is when waves pass an obstruction and move behind it. While there may be some diffraction of sound, the problem is focusing on the vibration of the tuning fork on the right. It is vibrating due to resonance because the frequency of the sound waves coming from the tuning fork on the left matches the natural frequency of the tuning fork on the right.